Al-Ḥusayniyyah Dome – Ta‛izz
جامع باعلوي- سيئون- حضرمو ت
Monument description
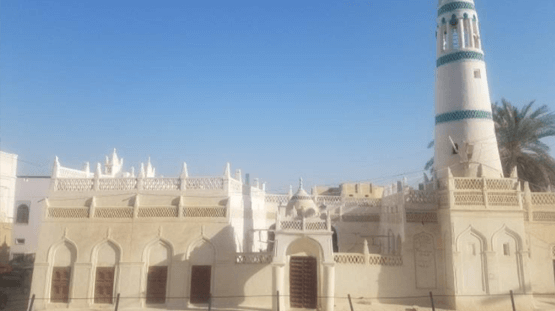
Ba-‘Alawi Mosque was constructed by Alawi bin Taha bin Al-Hassan bin Ahmed in 1072 AH. The Mosque was originally a small Mosque attached to the house of his grandfather Al-Hassan bin Ahmed in the neighborhood known as Suhail (Seiyun). The Mosque was also used for religious classes. The original small Mosque is now part of the Prayer Hall, which located opposite the Mihrab in the third portico.

Architectural and cultural value
Construction style and built date: Ba-Alawie Mosque is a model for mosques that belong to the late 12th century AH, or the Ottoman period. It is attributed to the master Alawi bin Taha bin Al-Hassan bin Ahmed Al-Habashi in the year 1072 AH. The mosque was renovated in Jumada I 1334 AH. It was renovated by Hassan bin Ahmed bin Ali bin Ahmed bin Abdullah bin Alawi bin Taha bin Al-Hasan bin Ahmed bin Muhammad Al-Habashi, and worked on build the fence wall (Al-Bustan).
Components of the Mosque: It consists of a Prayer Hall, a courtyard, annexes, a Minaret, and a water fountain. The area of the Monument with courtyard and annexes
is about 435 m2.
- Justifications for intervention:
- 1 – Carry out annual periodic maintenance works to preserve the mass of the building, especially the external surfaces and facades.
2 – Preserving the mosque as a traditional pattern in the mud architecture of Valley Hadramout.
3 – The mosque is considered as a model for Islamic monuments in the city in terms of rarity, authenticity and the time period in which this mosque was built.
- Monument conditions and treatment:
- The monument is damaged and there are many damages, including:
Serious damages:
1. Cracks and in the foundation of walls. Treatment: Repaint the base of the wall and sprinkle it with noura over it and use all the necessary materials to finish the work according to the principles of workmanship and according to the instructions of the supervising engineer.
2. Cracks and bulges in the external and internal walls. Treatment: Spray Al-Noura for external walls. The work includes using iron brush to remove the dust layer, maintain cracks and bulges in the damaged walls. Spray oil paint for windows and doors from the outside, and remove them as directed by the supervising engineer.
3. Cracks in the floors of the roof. Treatment: Surface maintenance work to prevent rainwater intrusion.

Countries












